Merge JSON to PDF
Overview
In this section, we explain the process of how to use JSON data and place dynamic content into the documents. Understanding this process allows users to create dynamic content with logical statements, dynamic tables and charts based on the JSON payload from the LaTeX templates.
JSON to Tex to PDF Workflow
DynamicDocs API incorporates R languarge to read the JSON data and places into R list of variables which is ready to use in the documents using functions from the knitr package.
In other words before converting the tex file into PDF with LaTeX, DynamicDocs API implements the R layer where R code is executed. The following sections we will show examples of making content dynamic. We assume that the user has a basic knowledge of R.
Available R Packages
The following list of R packages are loaded and their functions are readily available in the templates:
- Package knitr - Provides a general-purpose tool for dynamic report generation in R using Literate Programming techniques.
- Package base - Base R functions - This package contains the basic functions which let R function as a language: arithmetic, input/output, basic programming support, etc. Its contents are available through inheritance from any environment.
- Package stringi - Fast and Portable Character String Processing in R
- Package stringr - Simple, Consistent Wrappers for Common String Operations
- Package ggplot2 - Extra Themes, Scales and Geoms for 'ggplot2'
- Package ggthemes - Create Elegant Data Visualisations Using the Grammar of Graphics
- Package scales - Scale Functions for Visualization
- Package xts - Provide for uniform handling of R's different time-based data classes by extending zoo, maximizing native format information preservation and allowing for user level customization and extension, while simplifying cross-class interoperability.
- Package lubridate - Functions to work with date-times and time-spans: fast and user friendly parsing of date-time data, extraction and updating of components of a date-time (years, months, days, hours, minutes, and seconds), algebraic manipulation on date-time and time-span objects.
- Package kableExtra - Build complex'LaTeX' tables using 'kable()' from 'knitr' and the piping syntax from 'magrittr'. This package simplifies the way to manipulate the 'LaTeX' codes generated by 'kable()' and allows users to construct complex tables and customize styles using a readable syntax.
Note that due to AWS lambda limitations, the packages are restricted to the list above (apart from their dependencies which are also available).
TeX Live Distribution
TeX Live Distribution is the
Examples of Merging JSON to PDF
The primary way to include JSON data is with the use of knitr package and specifically the use of Sexpr function in the templates. In this section we will provide exampls of using this function to include strings, numerical values, dates and logical statements. For further resources on the knitr package, visit the following sources:
- Knitr Home Page - The package home page provides documentation with detailed options and examples for the package.
- Knitr on Stackoverflow - Questions on stackoverflow with knitr tag
- Dynamic Documents with R and knitr - Book by Yihui Xie
- Knitr Github - Knitr Github Page
Include Strings
In this example we show how to use the Sexpr function and include JSON string into the document.
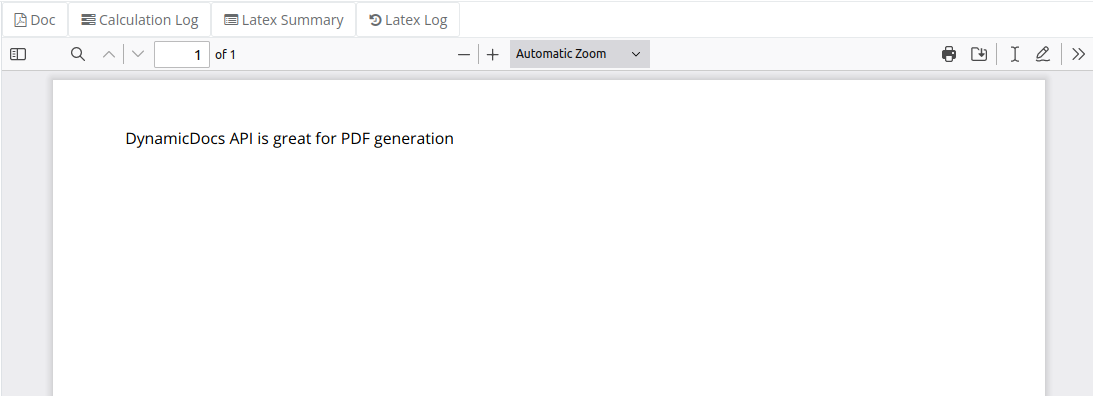
Notice that to retrieve the string value params$stringObject$string was used. All JSON values are retrived in the same manner.
Include Numerical Values
In this example we show how apply an R format function to the numerical value and display the output in the document, again with Sexpr function.
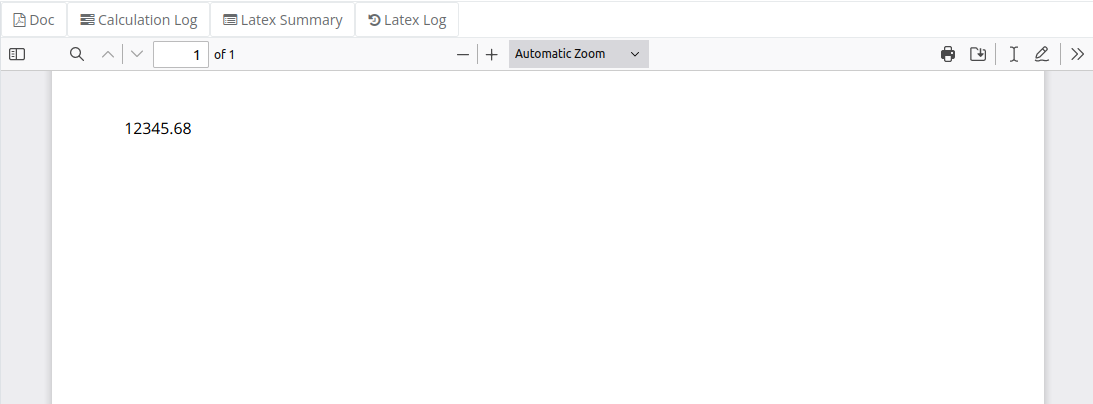
Notice that Sexpr function evaluates its content as if it was in R. In other words you can apply other R functions to the value as you see fit.
Include Dates
In this example we show how to convert JSON date and format it into the document.
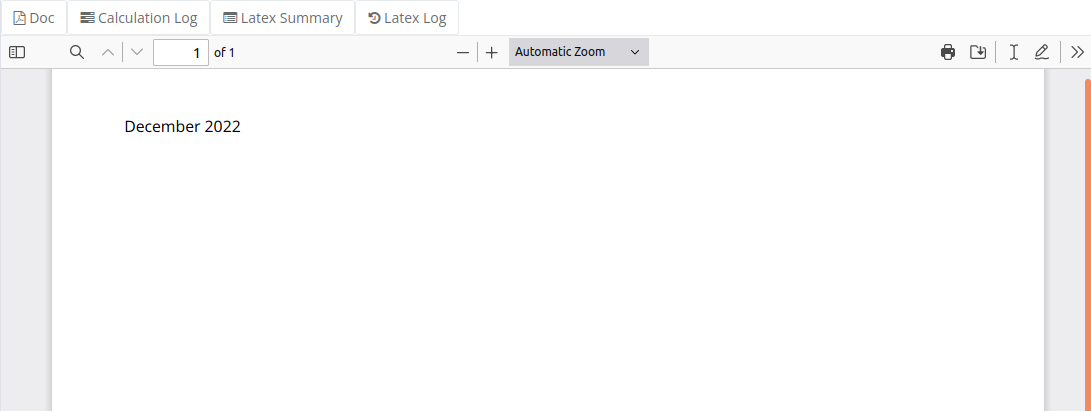
Include Logical Statements
In this example we show how to dispay text based on an if statement using the data in the JSON payload.
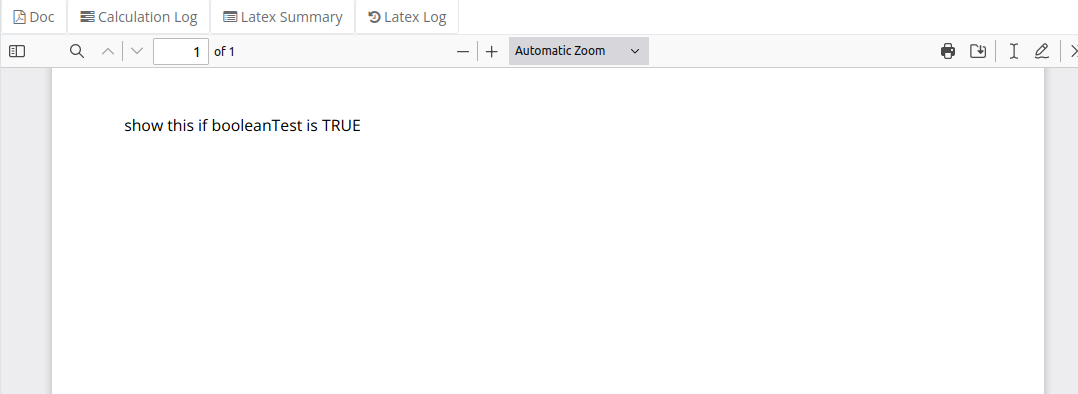
Note that you can use the if statement with R syntax and JSON data to create dynamic content in your template.
R Code in the Templates
The knitr package implements a coding architype known as Literate Programming. This feature combines code chunks (for computing) with LaTeX (pdf generation) in the same document. That is, the tex files can be injected with chunks of R code in order to run or perform more complex functions that need to be outputted in the PDF.
The general structure of a LaTeX file, which starts with the document class, however chunks of R code can be embedded within the code. These chunks are defined between two elements: <<…>> and @, which define the beginning and end of a chunk respectively. These two elements comprise of functions and R code that can be used in the document.
The following sections will show examples of using R code in the tex file to create custom functions and dynamic tables. For further information on using R code in the template file, refer to Knitr Package Home Page.
Include Custom Functions
In this example we show how to write custom function and create a new variable which is then used in the template to output it content.
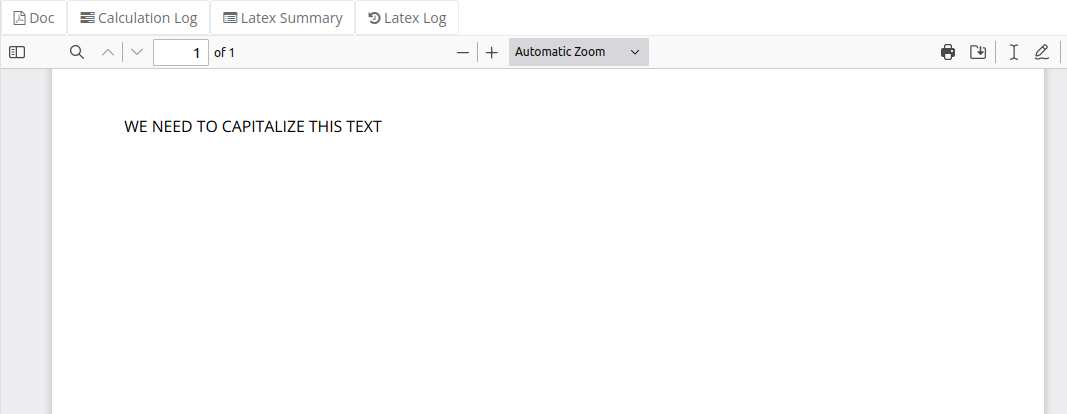
Include Tables
In this example we show how to use the kable function and create dynamic tables based on JSON payload.
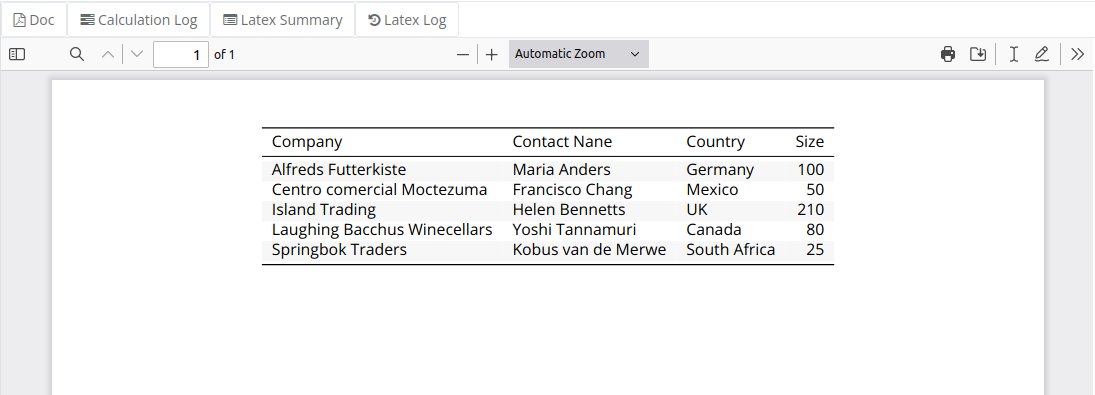
For further options on the kable function refer to the Package kableExtra reference manual and vignettes.
Include Charts
Charts which depend on the data in the JSON can be created using the ggplot2 package. For some examples visit the following Creating Charts page.